Why Important Wars from History Still Matter Today
Important Historical Wars: Numerous accounts of conflicts and battles that have transformed the world landscape are prevalent in history. Borders and headlines were but two consequences of these historical confrontations.
They founded nations, altered human conduct, and facilitated the emergence of the modern world.
Our examination of the greatest conflicts in history extends beyond mere battles. e are examining the causes,, resolutions, and enduring impacts of these conflicts.
Examine conflicts such as the Napoleonic Wars or battles that contributed to the formation and transformation of American history. These were not only historical narratives; they are events that continue to influence politics, alliances, and cultural standards now.
Every major fight, whether fought for power, money, or autonomy, exerted an influence. Each source contributes to the historical narrative of humanity, from the Persian Wars to contemporary events.
What insights can be gained from the study of major historical conflicts? A substantial amount of it! These conflicts elucidate the reasons behind the strength of certain states, the existence of specific alliances, and the persistence of hostilities in particular regions.
If these historical milestones captivate your curiosity, this book will navigate you through the conflicts that influenced the world. Let us analyze the rationale for the importance of each of these wars and their ongoing relevance.
Table of Contents
Defining Historical Wars and Their Global Importance

What Makes a War “Historical” and Why It Matters
When we talk about historical wars, we’re usually referring to conflicts that made a big impact on the world. These aren’t just ordinary skirmishes or short-term battles; they’re wars that changed things. Some altered borders, toppled governments, or left lasting scars on cultures. But what exactly makes a war “historical”?
A war is often considered historical if it left a major mark. It might have shifted the power of empires, changed the economy, or influenced culture in a way that still matters today. For example, wars like the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage shaped much of ancient Europe. Similarly, the American Revolutionary War didn’t just make America independent; it also set an example for other countries fighting for freedom.
These wars often show up in history books because of their lasting effects. But they’re more than facts on a page. Each war teaches us why humans fight, how societies survive, and what people believe is worth defending. Wars that are remembered today, the Thirty Years’ War or the Ottoman-Habsburg Wars or Ottoman-Habsburg-Wars, tell us stories of survival, resilience, and the power struggle.
The Types of Historical Wars
Not every war fits the same mold. Some wars were fought over land, others over ideas, and some even over religious beliefs. Here are a few major types of historical wars:
- Civil Wars: These are conflicts within a country, often between different groups or factions. The American Civil War is a well-known example that had huge consequences for the United States.
- Revolutionary Wars: These wars involve a fight for change or independence. The French Revolution and the American Revolution both reshaped societies and government systems.
- World Wars: These are the biggest conflicts, involving many countries. World Wars I and II changed not only the countries involved but also global politics.
- Colonial Wars: These wars were often about control over other lands or resources. Examples include the Seven Years’ War, which impacted Europe and its colonies, and the Reconquista in Spain.
Each type of war has its own reasons, outcomes, and lessons. By understanding these different wars, we get a fuller picture of why nations sometimes choose to fight.
Why Historical Wars Are Still Important Today
It may seem like these wars are old news, but their impact hasn’t faded. Many of the alliances and tensions we see around the world today started with these historical wars. For example, the alliances formed in WWII still affect which countries work together in global politics. Even conflicts from centuries ago, like the Crusades, still influence religious and cultural relationships in some regions.
These wars also show us the costs and consequences of conflict. By looking at how past societies dealt with war, we can learn ways to handle or prevent future conflicts. Studying historical wars gives us valuable insights, helping us understand why certain regions have lasting peace or struggle with ongoing disputes.
Ancient and Classical Era Wars (Before 500 CE)
How Ancient Wars Built Early Civilizations
In ancient times, wars weren’t just about grabbing power. They were about survival, growth, and often, the chance to create something new. These ancient wars played a huge role in shaping early civilizations, laying the groundwork for societies we know today. Each battle tells a story of building empires, defending lands, and developing the earliest strategies that would define warfare for centuries.
One of the earliest and most memorable conflicts was the Greco-Persian Wars. This was a series of intense battles between the Greek city-states—like Athens and Sparta—and the powerful Persian Empire. The Greeks fought hard for their independence, and against all odds, they won. Their victory didn’t just protect Greece. It also let Greek culture thrive, spreading ideas in art, philosophy, and government that continue to inspire modern society.
Another major clash in ancient Greece was the Peloponnesian War. Unlike the Greco-Persian Wars, this was a fierce battle for control between Athens and Sparta, the two most powerful city-states in Greece. This war was about dominance, not just defense. Both Athens and Sparta wanted to lead Greece, and their rivalry turned into years of bloody fighting. In the end, Sparta won, but Greece was left weakened and vulnerable to future enemies.
The Punic Wars: Rome vs. Carthage
Shifting to the western Mediterranean, we find the Punic Wars, a defining series of battles between Rome and Carthage. This conflict was all about control—of trade routes, territories, and influence in the region. Carthage, a powerful city in North Africa, was ideally placed for trade. But Rome wanted that influence for itself.
The most famous of these wars was the Second Punic War, where the Carthaginian general Hannibal led his army, including elephants, over the Alps to strike at Rome. Despite his surprising tactics and bravery, Rome ultimately won. This victory marked the start of Rome’s rise as a vast empire, giving it control over Europe, North Africa, and much of the Mediterranean.
Wars in the East: The Warring States Period in China
Ancient wars weren’t limited to Europe and the Mediterranean. In China, the Warring States Period was a long and intense era of conflict. For nearly two centuries, different states within China fought fiercely for control.
This period sparked the development of military strategies and ideas that are still famous today, like those in Sun Tzu’s The Art of War. Eventually, the Qin state emerged as the victor, leading to China’s unification and the start of the powerful Qin Dynasty.
Why Ancient Wars Still Matter Today
So, why should we care about wars that happened so long ago? These historical wars reveal the beginnings of military strategy, government, and the early connections between different societies. When empires won or lost, trade routes opened up, and with them came new ideas, religions, and technology that spread across continents.
For instance, if the Greeks hadn’t won the Greco-Persian Wars, Greek culture might not have spread as widely, changing the path of Western civilization.
Looking at these early conflicts also shows us that human societies have always been connected. Even in ancient times, wars in one part of the world could affect distant regions. This understanding makes history feel like a connected story that links the ancient past to the world we know today.
Middle Ages Warfare (500–1500 CE)

Defining Conflicts of the Middle Ages
The Middle Ages was an era marked by intense battles, conquests, and crusades that transformed Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. This period saw wars driven by religion, territory disputes, and political ambitions. Each conflict left a lasting impact on the people, cultures, and countries involved.
One of the defining wars of this era was the Crusades. These were a series of religious wars that started in the late 11th century, fought between Christians and Muslims. Their main goal? Control of Jerusalem and other holy sites. Knights, soldiers, and even ordinary citizens traveled from Europe to the Middle East to participate.
Though the Crusades ultimately failed to keep Jerusalem under Christian rule, they changed Europe forever. Trade routes opened, bringing new ideas, goods, and knowledge back to Europe from the East.
Meanwhile, in Asia, the Mongol Conquests were reshaping the continent. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan, the Mongols created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from China to Eastern Europe.
Although the Mongols’ methods were brutal, their conquests brought a period of relative stability called the Pax Mongolica. This era made trade along the Silk Road safer, connecting East and West and boosting cultural and economic exchanges.
The Hundred Years’ War: A Clash Between England and France
Another significant conflict of the Middle Ages was the Hundred Years’ War. This long struggle was fought between England and France, mainly over control of the French throne. Though it wasn’t a continuous battle, it spanned over a century, involving many clashes and notable figures, including Joan of Arc.
Joan of Arc became a symbol of French resistance during this war. She led French troops to key victories. They inspired her nation. But she was captured and executed.
Her bravery and sacrifice became legendary and contributed to France’s eventual victory. By the war’s end, England had lost most of its territories in France, and France had grown stronger and more unified.
The Reconquista: A Century-Long Struggle in Spain
In Spain, the Reconquista was a long war to reclaim land from Muslim rulers. From the early 700s until 1492, Christian kingdoms in Spain fought to push Muslim rulers southward. They eventually captured Granada, the last Muslim stronghold.
The Reconquista wasn’t just about territorial control. It helped shape Spain’s national identity and brought unity under Catholicism. Soon after, Spain became a powerful state. It was ready to explore and conquer lands across the Atlantic. This marked the start of its global empire.
Why These Middle Ages Wars Matter
The wars of the Middle Ages affected more than just borders. They influenced trade, culture, and even religion, leaving marks that still echo today. The Crusades brought new foods, fabrics, and ideas to Europe, sparking curiosity about the East.
The Mongol Empire linked distant lands. It let explorers like Marco Polo return with stories of Asia. These inspired future generations.
These wars also helped countries define their national identities. France’s victory in the Hundred Years’ War united its people, while the Reconquista helped forge a unified Spanish state. These wars show how medieval conflicts shaped the modern world. They influenced politics and cultural exchanges.
Early Modern Wars (1500–1800 CE)

The Wars That Shaped the Early Modern World
As nations began to form and empires expanded, the early modern era saw wars that left lasting marks on continents and cultures. These historical wars were fought not just for land but for ideology, religion, and global dominance. Each of these conflicts played a role in shaping the borders, governments, and societies we recognize today.
One of the most influential wars from this period was the Thirty Years’ War (1618–1648). This war began as a conflict between Catholic and Protestant states in the Holy Roman Empire but quickly spread across Europe. A religious struggle soon drew in many of Europe’s powerful nations, each pursuing its own political interests.
The war was devastating, with millions dead. It ended with the Peace of Westphalia, a treaty that founded modern state sovereignty. This peace agreement set a key principle. Each state has the right to govern itself without interference. This idea still influences international law today.
Another defining conflict was the Seven Years’ War (1756–1763). Often called the first “global war,” it involved most major European powers. It spread to North America, the Caribbean, India, and the Philippines.
The war pitted Britain and Prussia against France, Austria, and their allies, with battles on multiple continents. In North America, this conflict is known as the French and Indian War. The British emerged victorious, gaining control over large parts of North America and India.
However, the costs of the war led Britain to tax its American colonies, setting the stage for the American Revolutionary War.
The American Revolutionary War: The Birth of a Nation
The American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) was a fight for independence between Britain and its thirteen American colonies. Fueled by frustration over British taxation and a desire for self-rule, the colonies united against British rule. Key battles like those at Bunker Hill and Yorktown showcased the determination of the American forces.
The war ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1783, marking the birth of the United States as an independent nation. This conflict reshaped North America. It also inspired global independence movements. It showed that colonies could challenge and overthrow their imperial rulers.
The Ottoman-Habsburg Wars: A Struggle for European Dominance
As revolutions brewed in the West, the Ottoman-Habsburg Wars were a long struggle between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburgs. These wars lasted centuries. Each empire sought control of Eastern Europe. The Ottomans wanted to expand their empire into Europe. The Habsburgs fought to defend Christian lands.
Key battles like the Siege of Vienna in 1683 were turning points. The Ottomans were repelled, marking the start of their gradual decline. These wars changed the power balance in Europe. The Ottoman Empire weakened, allowing European powers to expand their influence in the region.
Why Early Modern Wars Matter Today
The early modern wars set the stage for the world as we know it. The Peace of Westphalia introduced state sovereignty. This principle still guides international relations. The American Revolution inspired democratic movements worldwide. It planted the seeds of freedom and self-governance.
These wars also reshaped economies, societies, and empires. The Seven Years’ War boosted Britain’s global influence, though its cost led to political upheaval. The Ottoman-Habsburg conflicts changed Europe’s power dynamics. They set the stage for future alliances and rivalries. These wars show how early modern conflicts shaped today’s nations, alliances, and global politics.
19th Century Conflicts

Wars of the 19th Century and the Rise of Nationalism
The 19th century was a time of intense change and upheaval. As nations sought independence or dominance, wars erupted across continents. Nationalism and a desire for self-rule often fueled these conflicts. These wars weren’t about territory. They were about identity, freedom, and reshaping empires.
One of the largest conflicts in this era was the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815). Led by Napoleon Bonaparte, France sought to expand its influence across Europe. Napoleon’s ambitions sparked a series of wars as he attempted to conquer various territories.
His campaigns stretched from Spain to Russia, reshaping the map of Europe and spreading ideas of the French Revolution. However, his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815 ended his reign and led to a period of peace in Europe through the Congress of Vienna, which aimed to balance power across nations and prevent future conflicts.
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was another pivotal conflict in the 19th century. This was a brutal internal struggle between the Northern and Southern states of the United States, primarily over slavery and state rights. The North fought to preserve the Union and end slavery, while the South fought to maintain its way of life. The Union’s victory in the war ended slavery and strengthened the government. The Civil War reshaped America. It set the country on a path to unity and industrial growth.
Wars for Independence in Latin America
The 19th century also saw numerous independence movements in Latin America. Inspired by the American and French Revolutions, South American colonies began to fight for freedom from Spanish and Portuguese rule.
Leaders like Simón Bolívar and José de San Martín led armies that defeated colonial powers. This led to the rise of independent nations, such as Venezuela, Argentina, and Colombia.
These wars were not only battles for land but also struggles for national identity. These revolutions succeeded. They inspired other colonies to seek independence.
The Crimean War: A Clash of Empires
The Crimean War (1853–1856) was a conflict between Russia and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, Britain, and France. The war, one of the first “modern” conflicts, was fought for control of territories around the Black Sea. It used new technologies like railroads, telegraphs, and rifles.
The Crimean War exposed the Russian Empire’s weaknesses. It led to reforms in Russia and changed how wars were fought. It also stressed the Black Sea region’s strategic importance. This focus is key in today’s geopolitics.
Why 19th Century Wars Still Matter
The wars of the 19th century didn’t just shift borders; they shifted ideologies. The Napoleonic Wars spread nationalism and revolutionary ideas across Europe. They inspired people to think about sovereignty and identity. The U.S. Civil War ended slavery. It set a global human rights precedent.
These wars also marked the rise of technology in warfare, as seen in the Crimean War. New weapons and strategies would shape conflicts in the next century. These 19th-century wars show that the fight for freedom and identity made the modern era.
Thank you for confirming. I’ll continue with the next section, “World Wars Era (20th Century),” using the guidelines.
World Wars Era (20th Century)
The Impact of the World Wars on Modern History
The 20th century saw two of history’s worst conflicts: World Wars I and II. These wars reshaped the world. They changed borders, ideologies, and social norms. Each global conflict left lasting marks. They still affect how nations interact today.
World War I (1914–1918), “The Great War,” began as a conflict between European powers. It quickly pulled in countries from around the world. It started with the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary. It grew into a struggle involving alliances and empires.
Trenches, chemical weapons, and machine guns turned battlefields into deadly landscapes. By the end of the war, millions had lost their lives, and the world was forever changed. The Treaty of Versailles ended the war. Its harsh terms fueled resentment in Germany, causing future unrest.
Only two decades later, the world faced another brutal war: World War II (1939–1945). This war saw Nazi Germany rise under Adolf Hitler. He sought to dominate Europe and impose his ideology. World War II saw brutal fighting and bombing.
The Holocaust killed six million Jews. The war saw new technologies, like tanks, aircraft, and, finally, the atomic bomb. With the defeat of Germany and Japan, the world split into two spheres of influence. The capitalist West, led by the U.S., and the communist East, led by the Soviet Union.
The Aftermath and Creation of the United Nations
One of the most significant outcomes of World War II was the creation of the United Nations (UN) in 1945. The UN wanted to stop future wars. It sought to promote cooperation and dialogue among nations. Its mission was to provide a platform for countries to resolve disputes peacefully. This would reduce the chance of global wars.
World War II’s end marked the start of the Cold War. It was a tense time between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. It was not a direct conflict. It was a political and ideological standoff. It influenced global politics for nearly half a century.
The Legacy of the World Wars
The World Wars changed more than just maps; they changed mindsets. World War I showed that large wars could harm entire populations. This led to efforts to promote peace and diplomacy. World War II showed the risks of unchecked power and ideology. It sparked global talks about human rights and international law.
These wars also spurred advances in technology, medicine, and industry. Wars increased the need for better medical care. This led to advances in surgery and emergency medicine. Wars drove tech innovations that built today’s key industries. They include aviation and nuclear energy.
The World Wars study shows today’s alliances and conflicts. It also shows today’s peacekeeping efforts. These lessons show the value of diplomacy and the costs of war. They also suggest that we can work together to prevent future conflicts.
Cold War Conflicts and Proxy Wars (1947-1991)
The Cold War and Its Global Impact
After World War II, the world split between two powers: the U.S. and the Soviet Union. This division sparked a long period of political and military tension known as the Cold War. It is not possible to remove the adverb.
They supported opposing sides in conflicts worldwide. These battles were often ideological. The U.S. promoted capitalism and democracy. The Soviet Union spread communism.
One of the earliest proxy conflicts was the Korean War (1950–1953). Korea was divided into a communist North, backed by the Soviets, and a democratic South, supported by the U.S. When the North invaded the South, the U.S. and other UN countries intervened.
This led to a brutal three-year war. The fighting ended in a ceasefire, but Korea is still divided. Tensions continue to this day.
Another key conflict of the Cold War was the Vietnam War (1955–1975). This was a lengthy, controversial conflict. North Vietnam, backed by the Soviet Union and China, fought South Vietnam and its main ally, the U.S.
The U.S. entered the war to stop communism’s spread. After years of fighting, it withdrew, and North Vietnam took control of the country. The Vietnam War deeply scarred American society. It showed the limits of military intervention.
The Soviet-Afghan War and Its Consequences
In the late 1970s, the Soviet Union entered a proxy war—the Soviet-Afghan War (1979–1989). The Soviet Union intervened to support Afghanistan’s communist government. It was fighting U.S.-backed mujahideen insurgents. This conflict drained Soviet resources and morale. It helped cause the Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991.
The Soviet-Afghan War had lasting consequences for the region. The fighters trained and funded by the U.S. later formed militant groups. Some of these groups would play major roles in future conflicts. This war serves as a reminder of how proxy wars can have unpredictable and lasting impacts.
The Nuclear Threat and Global Tensions
A defining feature of the Cold War was the nuclear arms race. Both the United States and the Soviet Union built large nuclear arsenals. This led to the policy of Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD).
This policy meant that any nuclear attack would destroy both sides. It effectively prevented direct conflict between the two superpowers. However, the constant threat of nuclear war kept the world on edge.
The Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962 brought the world close to nuclear disaster. The Soviet Union attempted to place nuclear missiles in Cuba, just miles from U.S. shores. The missiles were removed after tense talks. But the crisis showed the risks of nuclear escalation.
Why Cold War Conflicts Still Matter
The Cold War’s legacy is still evident today. It shaped global alliances and created lasting divisions. It also changed how countries approach diplomacy and conflict. Many alliances, like NATO, were formed then. They still shape global security.
These Cold War conflicts explain today’s regional tensions and ideological battles. The Cold War’s proxy wars, nuclear arms race, and politics left a complex legacy. It still affects international relations today.
Contemporary Conflicts (1991 – Present)
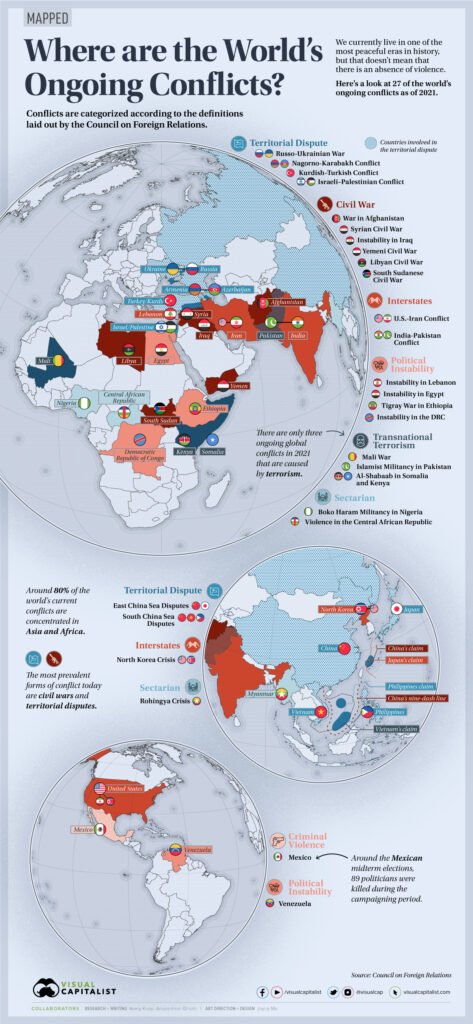
Modern Conflicts and Their Global Impact
The end of the Cold War brought significant changes to global politics, but it didn’t mean an end to conflict. Since 1991, new wars have emerged from regional disputes, terrorism, and shifting alliances. These contemporary conflicts have reshaped countries, sparked humanitarian crises, and altered international relationships.
One of the first major conflicts of this period was the Gulf War in 1990-1991. This war began when Iraq, under Saddam Hussein, invaded Kuwait. It sought to control Kuwait’s oil.
The U.N., led by the U.S., formed a coalition to oust Iraqi forces from Kuwait. The Gulf War was brief but highly televised. It showed the power of modern military technology and marked a new era in warfare.
Following the Gulf War, the War on Terror became a defining focus of global politics. The 9/11 attacks in 2001 spurred the U.S. to invade Afghanistan and then Iraq. The goal was to destroy terrorist networks and remove hostile regimes.
The Afghan War lasted over two decades, becoming America’s longest-running conflict. The 2003 Iraq War toppled Saddam Hussein. But it caused years of instability and civil unrest in the region.
The Syrian Civil War and the Rise of ISIS
The Syrian Civil War, which started in 2011, is one of the most devastating conflicts of recent years. It began as part of the Arab Spring, a wave of protests across the Middle East. In Syria, peaceful protests turned into armed conflict.
Various groups, including rebel factions, government forces, and extremists, fought for control. The war caused a huge humanitarian crisis. Millions fled the country, and there was widespread destruction.
During this period, a new threat emerged: ISIS (Islamic State of Iraq and Syria). ISIS took advantage of the chaos in Syria and Iraq, quickly seizing large territories. The group, known for its brutal tactics, declared a caliphate.
It then posed a major threat to regional and global stability. A coalition of countries pushed ISIS out of its territories. But its influence lingers through radicalized networks.
The Ukraine Crisis and Renewed Global Tensions
Another recent conflict that has captured global attention is the Ukraine Crisis. In 2014, tensions rose when Russia annexed Crimea. The world condemned the move. Since then, fighting has continued in Eastern Ukraine.
It is between Ukrainian forces and Russian-backed separatists. This conflict has raised worries about territorial disputes in Europe. It has also strained Russia’s relations with the US and EU.
The Ukraine conflict shows that Cold War issues still affect today’s geopolitics. The situation is complex. Economic sanctions, diplomacy, and military aid all fuel the tension.
Why Contemporary Conflicts Matter Today
Today’s conflicts are shaping the future of international relations. The War on Terror has changed countries’ security approaches. It has led to increased measures at home and abroad. The Syrian Civil War has caused a major refugee crisis. It shows the urgent need for humanitarian aid.
These modern conflicts remind us that global stability is fragile. Studying these wars helps us understand the conflict’s causes. It shows the need for diplomacy and cooperation to prevent future wars.
We must apply the lessons of recent conflicts. We face new challenges, like terrorism and regional disputes. They are more important than ever.
Key Themes and Lessons from Historical Wars

What We Can Learn from the Wars of the Past
Throughout history, wars have shaped the world in countless ways. Each conflict, whether ancient or modern, has left valuable lessons. Examining common themes in these wars helps us understand why they happened.
It also shows how they still affect us today. These insights also guide modern efforts in diplomacy, peacekeeping, and conflict prevention.
One recurring theme is the struggle for power and resources. The desire for land, wealth, or strategic advantage has driven many wars. For example, the Punic Wars were over trade routes.
The Napoleonic Wars aimed to expand French influence in Europe. This pattern shows how competition for resources can fuel conflict. It is a lesson still relevant today. Countries compete for valuable resources like oil and water.
Ideas have also been a powerful motivator in many wars. The Cold War was a fierce competition between two systems. Both the U.S. and the Soviet Union wanted to spread their beliefs worldwide. This led to conflicts in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan. This clash showed that differing beliefs can lead to long, bitter fights.
Lessons in Diplomacy and Cooperation
Another important lesson from historical wars is the value of diplomacy and alliances. Many wars ended not just through battles but through negotiations. The Peace of Westphalia ended the Thirty Years’ War. It set the foundation for modern diplomacy.
The Treaty of Versailles ended World War I. Its harsh terms later caused World War II. These examples show the need for fair treatment in peace deals. They also show the power of balanced agreements.
Alliances have also played a crucial role in historical conflicts. Countries that formed strategic partnerships often fared better in wars. During both World Wars, alliances determined which nations emerged victorious. Today, NATO shows this lesson. Countries can find stability and security by working together.
Understanding the Human Cost of War
Historical wars also teach us about the human cost of conflict. Wars have always brought suffering, from ancient battles to modern-day conflicts. World War II and the Holocaust remind us of war’s horrors.
The massive loss of life shows its devastation. The cost of war has led to international laws. They aim to protect civilians and prevent war crimes.
Studying the toll of past wars, we value peace more. We also see the need for conflict resolution. It reminds us that war’s effects extend beyond the battlefield. They impact generations to come.
Why These Lessons Matter Today
The themes and lessons from historical wars continue to influence modern society. We must learn why people went to war and how they ended. It will help us avoid repeating the same mistakes.
It shows the value of cooperation and the dangers of unchecked ambition. It also shows the need to respect cultural and ideological differences.
These lessons from the past aren’t just history—they’re guidelines for the future. As nations face new challenges, historical wars offer vital insights. They are key to a stable, peaceful world. This is amid resource shortages and ideological divides.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions on Important Historical Wars
1. What qualifies a war as “historical”?
A war is “historical” if it significantly impacted nations, cultures, or global relations. Wars change borders, economies, and ideologies. They influence the world for generations.
2. Which war had the most lasting impact on modern borders?
World War I significantly reshaped borders, especially in Europe and the Middle East. The Treaty of Versailles redrew maps, breaking up empires and creating new nations. These changes have influenced political tensions and alliances ever since.
3. Why are the World Wars considered so important?
The World Wars involved most major countries and led to unprecedented destruction. They also sparked major social, political, and economic changes. They ranged from the UN’s formation to shifts in global power.
4. How did ancient wars shape early civilizations?
Ancient wars, like the Greco-Persian and Punic Wars, helped develop early civilizations. These conflicts changed trade routes, governments, and cultures. They helped shape today’s societies.
5. What were the main causes of wars during the Cold War era?
Cold War conflicts were primarily driven by ideological differences between communism and capitalism. The U.S. and the Soviet Union often backed opposing sides in regional conflicts. They aimed to expand their influence. This led to proxy wars in Korea, Vietnam, and Afghanistan.
6. How did the Crusades affect Europe and the Middle East?
But the Crusades changed things. They opened trade routes between Europe and the Middle East. They boosted trade in goods and ideas. But they deepened cultural and religious divides that shaped future relations.
7. What are some examples of recent wars and their impact?
Recent conflicts, like the Syrian Civil War and the Ukraine Crisis, hurt global relations. These wars caused humanitarian crises and strained alliances. They raised concerns about human rights and stability.
Conclusion
Why Understanding Historical Wars Matters Today
Studying important historical wars helps us see the world through a clearer lens. These conflicts, ancient or modern, have shaped countries. They inspired revolutions and influenced today’s global relationships.
Each war, from the Napoleonic and American Revolutionary Wars to the recent War on Terror, shows something about human society.
Learning about these wars isn’t just about knowing who won or lost. It’s about knowing the reasons for each conflict and their lasting effects. For example, the World Wars taught us the value of alliances. The Cold War showed the power of ideological divides.
Reflecting on past conflicts reveals the causes of war. It shows the importance of peace and the value of cooperation. These lessons remind us to tackle global challenges wisely. We must choose diplomacy over conflict.
History often repeats itself. So, understanding the past can help us build a more peaceful future.
